User Ideas / Prospects
list of notable mechanical machines and tools, arranged in ascending order based on their approximate invention years.
1. Shaduf (~2000 BCE)

- Purpose: A lever-based irrigation tool used for lifting water, primarily in agriculture.
- Category: Agricultural.
2. Plow (~3000 BCE)
- Purpose: A farming tool for tilling the soil, one of the earliest mechanical agricultural tools.
- Category: Agricultural.
3. Water Wheel (~400 BCE)

- Purpose: Used in ancient Greece and Rome to harness water power for grinding grain and performing mechanical tasks.
- Category: Agricultural and Industrial.
4. Archimedes' Screw (~250 BCE)

- Purpose: A mechanical device for lifting water, used for irrigation.
- Category: Agricultural.
5. Catapult (~400 BCE)

- Purpose: A military machine used for launching projectiles in battle.
- Category: Military.
6. Ballista (~400 BCE)

- Purpose: An ancient missile weapon, similar to a large crossbow, for military use.
- Category: Military.
7. Windmill (~500-900 CE)

- Purpose: A mechanical device to harness wind power for grinding grain or pumping water.
- Category: Agricultural and Industrial.
8. Spinning Wheel (~1000 CE)

- Purpose: A tool for spinning thread or yarn from natural fibers, significantly improving textile production.
- Category: Textile.
9. Mechanical Clock (~1300 CE)

- Purpose: Used to measure time with increased precision, widely installed in public spaces.
- Category: Common use, scientific.
10. Printing Press (1440 CE)

- Inventor: Johannes Gutenberg.
- Purpose: Revolutionized the production of books and the dissemination of information through mechanical printing.
- Category: Industrial.
11. Flying Shuttle (1733 CE)

- Inventor: John Kay.
- Purpose: A key development in the textile industry, it sped up the weaving process in looms.
- Category: Textile.
12. Spinning Jenny (1764 CE)
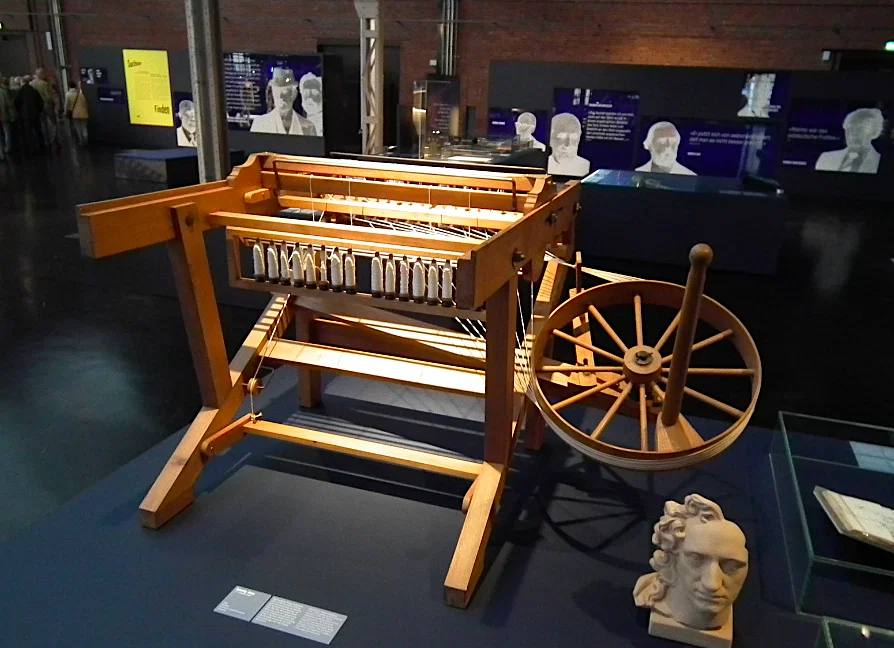

- Inventor: James Hargreaves.
- Purpose: A multi-spindle spinning frame, dramatically increasing the production of yarn.
- Category: Textile.
13. Water Frame (1769 CE)

- Inventor: Richard Arkwright.
- Purpose: A water-powered spinning machine that was crucial for mechanizing the textile industry.
- Category: Textile.
14. Spinning Mule (1779 CE)

- Inventor: Samuel Crompton.
- Purpose: Combined the features of the Spinning Jenny and the Water Frame, producing finer, stronger thread.
- Category: Textile.
15. Steam Engine (1698-1712 CE)

- Inventor: Thomas Savery (1698), improved by Thomas Newcomen (1712) and James Watt (1765).
- Purpose: Used for pumping water, powering textile mills, and eventually revolutionizing transportation.
- Category: Industrial, transportation.
16. Power Loom (1785 CE)
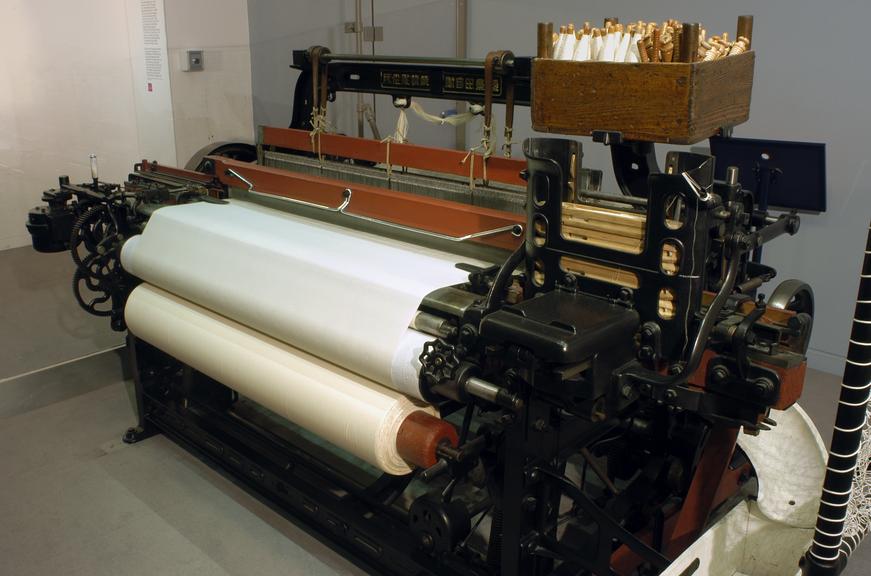

- Inventor: Edmund Cartwright.
- Purpose: A mechanized loom that revolutionized the weaving process, contributing to the rise of factory-based textile production.
- Category: Textile.
17. Lathe (~1500 CE, modern lathe in 1750s)

- Purpose: A machine tool for shaping wood or metal, used in various industries including textiles for creating components.
- Category: Industrial.
18. Jacquard Loom (1804 CE)
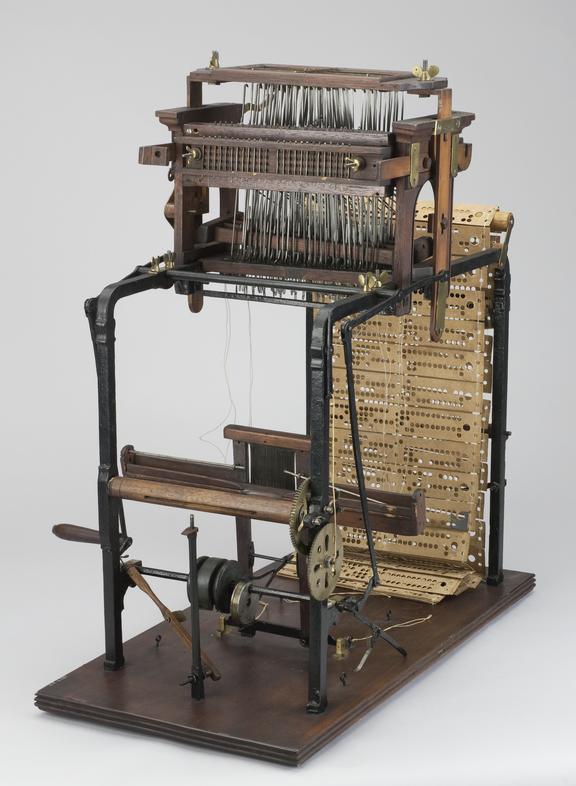

- Inventor: Joseph Marie Jacquard.
- Purpose: Introduced a punch-card system to control the weaving of complex patterns in textiles, an early precursor to programming.
- Category: Textile.
19. Treadle-Powered Sewing Machine (1830 CE)

- Inventor: Barthelemy Thimonnier.
- Purpose: Mechanized sewing, revolutionizing garment manufacturing.
- Category: Textile, domestic.
20. Steam Locomotive (1804 CE)

- Inventor: Richard Trevithick.
- Purpose: Powered by steam engines, it transformed transportation and logistics.
- Category: Transportation.
21. Internal Combustion Engine (1876 CE)
- Inventor: Nikolaus Otto.
- Purpose: Powered automobiles and machinery, driving the transportation revolution.
- Category: Industrial, transportation.
22. Automobile (~1886 CE)
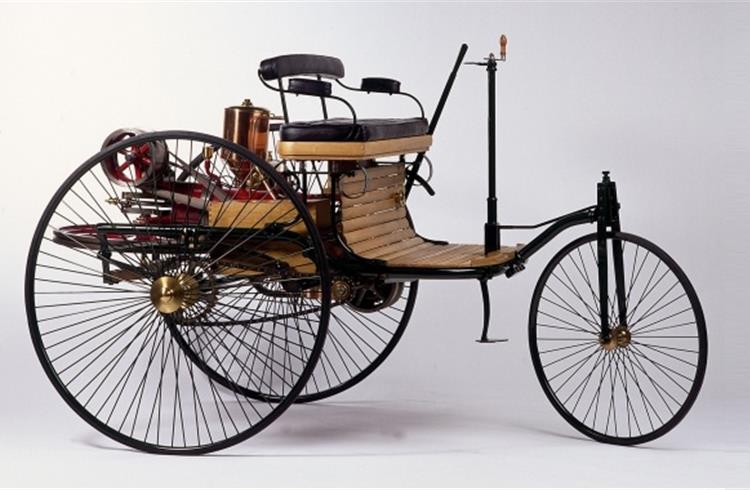

- Inventor: Karl Benz.
- Purpose: The first practical gasoline-powered car.
- Category: Transportation.
23. Airplane (1903 CE)

- Inventor: Wright Brothers.
- Purpose: The first powered flight, leading to modern aviation.
- Category: Transportation.
This timeline shows how early mechanical innovations in agriculture and military evolved into textile industry machines, which were a major part of the Industrial Revolution. Later, broader industrial machinery and transportation innovations took over, shaping the modern world.
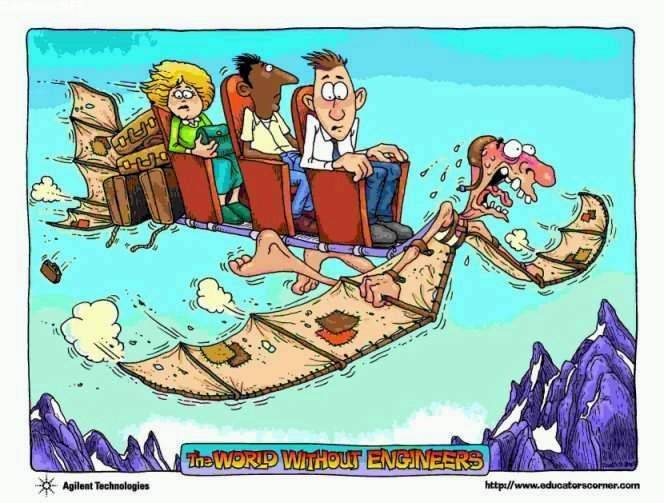
how life would be impacted without engineers from various specialized fields
- Infrastructure: Civil engineers design, build, and maintain essential infrastructure like roads, bridges, dams, and buildings. Without them, our transportation networks would be rudimentary, buildings less safe, and urban planning chaotic.
- Water Resources: Civil engineers also handle water supply and sanitation systems. Without them, clean water would be scarce, and sanitation could be a major public health crisis.
- Urban Development: City planning and the development of sustainable communities would be hindered, leading to overcrowded and poorly organized living spaces.
- Machinery and Automation: Mechanical engineers design and develop machines used in industries, transport, and everyday life. Without them, there would be no cars, trains, or airplanes, and industrial processes would be inefficient and labor-intensive.
- Energy Systems: Mechanical engineers also work on power generation systems like turbines and engines. Without them, our ability to generate and efficiently use energy would be severely limited.
- Consumer Products: From home appliances to fitness equipment, many everyday items would be unavailable or far less effective.
- Power Generation and Distribution: Electrical engineers design and maintain the systems that generate and distribute electricity. Without them, we’d lack reliable power, leading to a return to pre-electricity lifestyles.
- Communication Systems: Electronics engineers develop the technology behind phones, computers, and the internet. Without their work, global communication would be nearly impossible.
- Automation and Control Systems: Modern factories and homes rely on automation for efficiency. Without these engineers, production and daily life would be far less efficient.
- Computing Devices: Computer engineers are behind the development of hardware and software that powers computers, smartphones, and other digital devices. Without them, we’d be without modern computing, crippling almost every industry.
- Networking and Internet: They also design the systems that make the internet possible. Without these, global connectivity and access to information would be severely restricted.
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics: Advancements in AI and robotics, which are revolutionizing industries, wouldn’t exist without computer engineers.
- Pharmaceuticals: Chemical engineers are crucial in the production of medicines. Without them, the development and mass production of life-saving drugs would be impossible.
- Petroleum and Energy: They also work in refining petroleum and developing alternative energy sources. Without them, fuel would be less accessible, and energy innovation would stagnate.
- Food Processing: The food we eat often requires processing to be safe and palatable. Chemical engineers ensure that food products are safe, nutritious, and efficiently produced.
- Aviation: Aerospace engineers design and develop aircraft. Without them, air travel wouldn’t exist, drastically limiting global mobility.
- Space Exploration: They are also responsible for spacecraft and satellite technology. Without aerospace engineers, humanity’s exploration of space and our understanding of the universe would be non-existent.
- Defense: Many defense systems, including missiles and surveillance drones, rely on aerospace engineering. Without this expertise, national security could be compromised.
- Medical Devices: Biomedical engineers design and develop medical devices like pacemakers, MRI machines, and prosthetics. Without them, diagnosing and treating many conditions would be much harder or impossible.
- Tissue Engineering: Advances in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are spearheaded by biomedical engineers. Without them, treatments that restore or replace damaged tissues wouldn’t be available.
- Healthcare Innovation: The continuous improvement of healthcare technologies, leading to better patient outcomes, depends heavily on biomedical engineers.
- Pollution Control: Environmental engineers develop systems to reduce pollution and manage waste. Without them, air, water, and soil contamination would be far worse, endangering human health and ecosystems.
- Sustainable Development: They also work on projects that aim to balance development with environmental protection. Without their expertise, sustainability efforts would falter, leading to resource depletion and ecological crises.
- Renewable Energy: Environmental engineers are key in developing and implementing renewable energy solutions, crucial for combating climate change. Without them, the transition away from fossil fuels would be significantly slower.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Industrial engineers optimize production processes, ensuring that goods are made efficiently and cost-effectively. Without them, manufacturing would be slower, more expensive, and less reliable.
- Supply Chain Management: They also manage supply chains, ensuring that products are delivered on time and at the right cost. Without industrial engineers, logistics would be chaotic, leading to shortages and inefficiencies.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet quality standards is another key role. Without industrial engineers, product defects would be more common, affecting safety and customer satisfaction.
- Advanced Materials: Materials engineers develop new materials with specific properties for various applications. Without them, innovations in electronics, construction, and healthcare (like biodegradable implants) would be impossible.
- Metallurgy: They also work on the extraction and processing of metals. Without them, we would lack the materials needed for building infrastructure, manufacturing tools, and producing electronics.
- Nanotechnology: Advancements in nanotechnology, leading to innovations in fields like medicine, electronics, and energy, are driven by materials engineers. Without them, many cutting-edge technologies would not exist.
- Farm Equipment: Agricultural engineers design and develop machinery used in farming. Without them, modern farming methods wouldn’t be possible, leading to less food production and higher food prices.
- Irrigation and Water Management: They also design systems for efficient water use in agriculture. Without these systems, crop yields would be lower, and water resources could be wasted.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Agricultural engineers are involved in developing sustainable farming practices to ensure food security. Without them, agriculture would struggle to meet the demands of a growing population.
- Shipbuilding: Marine engineers design and maintain ships and submarines. Without them, maritime trade and naval defense would be greatly diminished.
- Offshore Engineering: They also work on offshore structures like oil rigs and wind farms. Without marine engineers, exploiting marine resources and developing offshore energy would be nearly impossible.
- Oceanographic Technology: Marine engineers contribute to technologies that explore and monitor the ocean. Without their work, our understanding and stewardship of marine environments would be limited.
- Soil and Rock Mechanics: Geotechnicalengineers study the behavior of earth materials. Without them, constructing stable foundations for buildings, bridges, and tunnels would be much riskier.
- Landslide and Earthquake Mitigation: They also develop solutions to mitigate landslides and earthquake impacts. Without geotechnical engineers, many areas would be unsafe for habitation.
- Mining Engineering: Extraction of minerals and resources from the earth is guided by geotechnical principles. Without these engineers, mining would be far less efficient and more dangerous.
Without engineers from these specialized faculties, the world would lack the technological advancements, infrastructure, and innovations that make modern life possible. Society would struggle with basic needs like shelter, transportation, healthcare, and communication, resulting in a world that is less safe, less connected, and less prosperous.
Image Describes Human Civilization WIth and Without Engineers and all the advancement through them
Life without engineers would be drastically difficult, as engineers play a critical role in shaping the world we live in. Here are some key aspects that would be affected:
Infrastructure: Cities would lack the essential infrastructure like bridges, roads, tunnels, and buildings. The absence of civil engineers would mean no skyscrapers, efficient transportation systems, or safe residential structures.
Technology: Without engineers, technological advancements would be minimal. Computers, smartphones, and the internet—integral to modern communication—wouldn't exist.
Energy: Our energy systems, from electricity grids to renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines, rely heavily on engineers. Without them, reliable power supply and modern conveniences like electric lighting and heating would be unavailable.
Healthcare: Medical devices, diagnostic equipment, and pharmaceutical production processes, all designed and maintained by biomedical and chemical engineers, would be non-existent. This would significantly hinder medical progress and healthcare quality.
Transportation: Cars, airplanes, trains, and ships, all products of mechanical and aerospace engineering, would not exist. Travel would be limited to primitive methods, drastically slowing down global mobility.
Manufacturing: The production of goods, from food processing to electronics, relies on sophisticated machinery and automation designed by engineers. The efficiency and scale of modern manufacturing would be impossible without their contributions.
Water and Sanitation: Engineers design systems to provide clean water and manage waste. Without these systems, public health would be severely compromised.
Communication: The development of telecommunication systems, including satellites and fiber optics, would stall without engineers, limiting global connectivity.
Engineers are the backbone of innovation and functionality in society. Their absence would result in a world where basic needs are hard to meet, and technological progress is stunted.
So thanks to all the engineers to make Human Civilization more wonderful, good and easy going with full of facility and luxury.
Long Live Engineering
Now before you readers get this to some other way I must want to admit that. Science itself is more than just a philosophy. Even without direct engineering applications, scientific research advances our understanding of the universe, which is valuable in its own right. Pure science often drives innovation by pushing the boundaries of knowledge, which engineers later translate into practical applications.
The relationship between science and engineering is symbiotic rather than hierarchical. Engineers rely on scientific discoveries to innovate, and scientists often depend on engineering tools and technologies to conduct research. For example, advances in materials science or biomedical research often require sophisticated engineering tools and techniques.
And like wise Scientific research often relies on advanced tools and instruments, many of which are developed by engineers. For instance, modern physics would be unimaginable without the sophisticated particle accelerators designed by engineers, which allow scientists to probe the fundamental nature of matter.
Many scientific fields, such as astronomy or genomics, generate vast amounts of data. Engineers develop the technologies—like telescopes, sequencing machines, and data processing software—necessary for collecting, storing, and analyzing this data, enabling scientific discoveries.
Engineering innovations frequently lead to new experimental techniques. For example, advancements in materials science, a branch of engineering, have allowed scientists to explore the properties of new materials, leading to discoveries in nanotechnology and quantum computing.
Science provides the theoretical foundation and discoveries that engineers use to develop new technologies, while engineering provides the tools, techniques, and innovations that enable scientific research to advance. Both fields are crucial for progress, and each drives the other forward, leading to the continuous evolution of knowledge and technology.
So Science and Engineering both are interdependent wise versa.
but still ...
Engineers are responsible for applying scientific principles to solve real-world problems. Science provides the foundational knowledge, but engineering turns that knowledge into practical solutions, such as technology, infrastructure, and systems that benefit society. Without engineering, scientific discoveries might remain theoretical concepts, with limited impact on everyday life.
Engineers bridge the gap between scientific theory and practical implementation. For instance, while scientists may understand the principles of electromagnetism, it’s engineers who design and build electrical grids, smartphones, and computers. This practical application is what transforms scientific ideas into tangible realities.
Engineering is crucial for innovation and technological progress. Many of the advancements we associate with modern science—such as medical devices, renewable energy systems, and communication technologies—are the result of engineering efforts to harness scientific discoveries.
So "Without Engineers, Science Is Just a Philosophy" is a significant truth.
so I wrote this article to dedicate my gratitude to all of the Engineers who work hard on big important project with knowing that their name probably not going to shine only money as per market norm they are going to get but still they did work harder and smarter to make sure project don't get failed.
Long Live Engineering.
- Description: These kits typically include components like gears, pulleys, levers, and inclined planes. They are used to demonstrate fundamental mechanical principles such as force, torque, motion, and energy transfer.
- Common Uses: Educational demonstrations, basic experiments in statics and dynamics.
- Tools and Components:
- Gears (spur, bevel, worm)
- Pulleys and belts
- Levers and fulcrums
- Inclined planes
- Springs and weights
- Ropes and strings
- Force gauges
- Screw sets and nuts
- Description: Kits designed to study the motion of mechanisms, including linkages, cams, gears, and various types of motion converters (linear to rotational, etc.).
- Common Uses: Analysis of motion, design of mechanical linkages, study of velocity and acceleration in mechanical systems.
- Tools and Components:
- Linkages (four-bar, slider-crank)
- Cams and cam followers
- Gears and gear trains
- Shafts and axles
- Bearings
- Rotary encoders
- Stopwatches
- Protractors and rulers
- Description: These kits may include components like heat exchangers, thermocouples, and various setups to study conduction, convection, and radiation. They are used to demonstrate and experiment with the principles of thermodynamics and heat transfer.
- Common Uses: Demonstrating laws of thermodynamics, studying energy conversion processes, heat transfer experiments.
- Tools and Components:
- Heat exchangers
- Thermocouples and thermometers
- Insulating materials
- Heating elements (electric heaters, Bunsen burners)
- Calorimeters
- Pressure gauges
- Fans and blowers (for convection experiments)
- Radiation plates and sensors
- Description: Kits that include components like pumps, turbines, pipes, and flow meters. They are used to study fluid flow, pressure, and fluid-structure interactions.
- Common Uses: Demonstrating Bernoulli’s principle, studying laminar and turbulent flow, analyzing fluid systems.
- Tools and Components:
- Pumps (centrifugal, positive displacement)
- Flow meters (Venturi, orifice plate, rotameter)
- Piping and tubing
- Manometers and pressure gauges
- Valves (gate, ball, check)
- Turbines (small-scale)
- Nozzles and diffusers
- Fluid reservoirs
- Description: These kits typically include motors, sensors, controllers, and structural components to build and program robots. They may also come with software for simulation and control.
- Common Uses: Designing and programming robots, studying kinematics, automation, and control systems.
- Tools and Components:
- Servo motors and DC motors
- Microcontrollers (Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Sensors (ultrasonic, infrared, light)
- Wheels and tracks
- Structural components (beams, plates, fasteners)
- Breadboards and jumper wires
- Battery packs and power supplies
- Programming cables
- Description: Kits that provide components such as servos, controllers, sensors, and feedback devices to study control theory and implement control systems.
- Common Uses: PID controller experiments, stability analysis, automation tasks.
- Tools and Components:
- PID controllers
- Servos and actuators
- Sensors (temperature, pressure, position)
- Control loops (analog and digital)
- Microcontrollers or PLCs
- Oscilloscopes
- Signal generators
- Relay modules and switches
- Description: Kits that allow the study of vibrational characteristics of mechanical systems. They typically include components for generating and measuring vibrations, such as accelerometers, mass-spring systems, and damping materials.
- Common Uses: Studying natural frequencies, damping, and resonance in mechanical structures.
- Tools and Components:
- Accelerometers
- Vibration motors
- Springs and masses
- Damping materials (rubber pads, foam)
- Frequency counters
- Shakers (vibration generators)
- Signal analyzers
- Tunable mass dampers
- Description: These kits may include samples of different materials, testing equipment (like hardness testers), and tools for analyzing material properties such as tensile strength, elasticity, and fracture toughness.
- Common Uses: Material testing, failure analysis, studying the properties of metals, polymers, and composites.
- Tools and Components:
- Universal Testing Machine (UTM) components
- Hardness testers (Rockwell, Brinell)
- Sample materials (metals, polymers, composites)
- Microscopes (optical)
- Strain gauges
- Impact testers
- Metallurgical mounts
- Fracture analysis tools
- Description: Kits that include components like gears, shafts, bearings, and fasteners to design and test mechanical assemblies and systems. They may also include CAD files for 3D modeling.
- Common Uses: Prototyping mechanical systems, studying load distribution, stress analysis, and design optimization.
- Tools and Components:
- Gears (spur, helical, worm)
- Shafts and keys
- Bearings (ball, roller)
- Fasteners (bolts, nuts, washers)
- Sprockets and chains
- Couplings (rigid, flexible)
- Belts and pulleys
- Tolerance gauges and calipers
- Description: Kits focused on the principles of energy conversion, including components like solar panels, wind turbines, and small-scale engines. They are used to study and experiment with converting energy from one form to another.
- Common Uses: Experiments in renewable energy, studying thermodynamic cycles, efficiency analysis.
- Tools and Components:
- Small solar panels
- Wind turbine models
- Electric generators and motors
- Thermoelectric generators
- Batteries and energy storage devices
- Inverters and converters
- Energy meters and sensors
- Thermal engines (Stirling, steam)
- Description: Small-scale CNC kits that include a computer-controlled milling machine or lathe, along with the necessary software and tooling. These kits are used to introduce students and hobbyists to CNC machining.
- Common Uses: Prototyping, precision machining, learning CNC programming.
- Tools and Components:
- CNC milling machine or lathe
- Cutting tools (end mills, drill bits)
- Tool holders and collets
- Workholding devices (clamps, vises)
- Coolant system (basic)
- CAD/CAM software
- G-code generator
- Safety glasses and gloves
- Description: Kits that include a 3D printer and materials like PLA, ABS, or resin. These kits are used for prototyping and studying the principles of additive manufacturing.
- Common Uses: Rapid prototyping, custom part manufacturing, studying additive manufacturing processes.
- Tools and Components:
- 3D printer (FDM or resin)
- Filament or resin material
- Build plate and adhesives
- Nozzles and extruders
- CAD software
- Calibration tools (bed levelers, gauges)
- Scrapers and cutters (for part removal)
- UV light (for resin curing)
- Description: These kits include pumps, cylinders, valves, and actuators to demonstrate hydraulic and pneumatic systems. They are used to study the principles of fluid power and control.
- Common Uses: Building and controlling fluid power systems, studying hydraulic and pneumatic actuators.
- Tools and Components:
- Hydraulic pumps and cylinders
- Pneumatic actuators and valves
- Hoses and fittings
- Pressure gauges
- Flow control valves
- Reservoirs
- Compressors
- Control panels (manual or automated)
- Description: Kits designed to explore renewable energy technologies, often including small-scale solar panels, wind turbines, and associated measurement tools.
- Common Uses: Experiments in renewable energy generation, studying energy efficiency, and sustainability.
- Tools and Components:
- Small wind turbine blades and generator
- Solar panels
- Inverters and charge controllers
- Battery packs
- Energy meters
- Load resistors (for testing)
- Mounting hardware
- Simulation software (optional)
- Description: Kits that simulate automotive systems, including components like small engines, transmissions, braking systems, and suspension models.
- Common Uses: Studying vehicle dynamics, engine performance, and automotive systems design.
- Tools and Components:
- Small-scale engines (gasoline, electric)
- Transmission models
- Suspension systems (springs, dampers)
- Braking systems (disk, drum)
- Steering mechanisms Models
- Differential models
- Diagnostic tools (multi-meters, OBD scanners)
- Fuel and exhaust systems (carburetors, mufflers)
These kits are valuable resources for hands-on learning, experimentation, and the application of mechanical engineering principles in real-world scenarios.
common engineering jobs along with their primary subject matter expertise and essential skills that are considered foundational or "bread and butter" for each role:
All of listed expertise or knowledge are not written as each and every one of them are compulsory but at least 2-3 of them must have for advancement or progress in my opinion.
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Materials Science
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software (e.g., SolidWorks, AutoCAD)
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- Fluid dynamics and heat transfer
- Mechanical systems design and analysis
- Manufacturing processes and materials selection
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Circuit Design, Electromagnetism, Power Systems
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Circuit analysis and design
- PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design and layout
- Control systems engineering
- Embedded systems and microcontroller programming
- Power generation and distribution
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Structural Analysis, Geotechnics, Fluid Mechanics
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Structural design and analysis (e.g., using software like SAP2000, ETABS)
- Surveying and mapping techniques
- Soil mechanics and foundation design
- Hydraulics and water resources engineering
- Construction management and materials
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Algorithms, Data Structures, Software Development
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Programming languages (e.g., Python, Java, C++)
- Software development methodologies (Agile, Scrum)
- Version control systems (e.g., Git)
- Data structures and algorithms
- Database management (SQL, NoSQL)
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Chemical Reactions, Process Design, Thermodynamics
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Process simulation software (e.g., Aspen HYSYS, CHEMCAD)
- Chemical reaction engineering
- Heat and mass transfer
- Process control and instrumentation
- Safety and environmental regulations in chemical processes
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Aerodynamics, Propulsion, Structural Analysis
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Aerodynamics and fluid dynamics
- Structural analysis for aerospace applications
- Propulsion systems (e.g., jet engines, rockets)
- Flight mechanics and control
- Materials science for aerospace (e.g., composites, alloys)
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Process Optimization, Operations Research, Human Factors
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Process improvement techniques (Lean, Six Sigma)
- Operations research and optimization
- Supply chain management
- Human factors and ergonomics
- Statistical analysis and quality control
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Environmental Science, Water Resources, Waste Management
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Environmental impact assessment
- Water and wastewater treatment processes
- Air quality management
- Waste management and remediation techniques
- Regulatory compliance and sustainability practices
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Biomedical Devices, Biomechanics, Systems Biology
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Medical device design and testing
- Biomechanics and biological systems modeling
- Imaging and signal processing
- Biomaterials and tissue engineering
- Regulatory standards and medical ethics
- Primary Subject Matter Expertise: Materials Science, Metallurgy, Polymer Science
- Bread and Butter Skills:
- Material characterization techniques (e.g., X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy)
- Metallurgy and materials selection
- Polymer and composite materials design
- Failure analysis and materials testing
- Development of new materials and coatings
These core skills are essential for professionals in these roles and are often the foundation for further specialization within their respective fields.
there is huge gap between these two and thats actually leads to unemployment in engineering fields although there are lots of scope to work as an engineer but still lots of vacancy is not getting fulfilled and people get unemployed even though they got degree.
Academic Engineering and Industrial Engineering represent two distinct spheres within the broader field of engineering, each with its own focus, goals, and approaches. Here's a breakdown of the key differences between the two:
1. Purpose and FocusAcademic Engineering:
- Purpose: Focuses on the theoretical, scientific, and educational aspects of engineering. It aims to expand knowledge through research, teaching, and the development of new theories and methodologies.
- Focus: In-depth exploration of fundamental principles, mathematical modeling, simulations, and theoretical analysis. Academic engineers often work on advancing the frontiers of knowledge in their field.
Industrial Engineering:
- Purpose: Concerned with applying engineering principles to optimize processes, systems, and organizations within industries. The goal is to improve efficiency, productivity, and quality in real-world applications.
- Focus: Practical implementation of engineering knowledge in manufacturing, logistics, supply chain management, and operations. Industrial engineers work to solve practical problems and enhance industrial processes.
Academic Engineering:
- Research: Typically involves basic or fundamental research aimed at discovering new knowledge without immediate commercial application. Academic research often leads to publications in scientific journals and conferences.
- Development: May involve the development of new theories, algorithms, or techniques that contribute to the academic body of knowledge. Development is usually more conceptual and less concerned with immediate industrial application.
Industrial Engineering:
- Research: Focuses on applied research that directly addresses industry-specific challenges. Research is often driven by the need to solve specific problems or improve existing processes within a company or sector.
- Development: Involves the design, implementation, and optimization of processes, systems, or products. Development is closely tied to practical outcomes and often leads to new products, improved systems, or increased efficiency.
Academic Engineering:
- Application: Knowledge is applied primarily in an educational setting (teaching) or within research labs. The results may influence industrial practices but are often several steps removed from direct application.
- Outcome: Contributes to the theoretical foundation and future technologies. The impact on industry is typically long-term, as academic findings may take years to be applied.
Industrial Engineering:
- Application: Directly applies engineering principles to solve problems within industry. Industrial engineers work on projects that have immediate or short-term impacts on the company’s operations.
- Outcome: Results in tangible improvements in processes, cost savings, enhanced productivity, and quality within a relatively short timeframe.
Bridging the gap between academic engineering and industrial engineering can enhance innovation, improve practical outcomes, and ensure that theoretical advances translate effectively into real-world applications. Here are some strategies to help fulfill this gap:
1. Collaborative Research Initiatives- Industry-Academia Partnerships: Encourage collaborations between universities and industry to work on joint research projects. Companies can provide practical problems, while academic researchers can offer theoretical insights and advanced methodologies.
- Sponsored Research: Industries can sponsor research at universities focused on specific challenges they face. This ensures that academic research is aligned with industrial needs.
- Academic Internships: Encourage students and faculty to engage in internships or sabbaticals in industrial settings. This exposes academics to real-world challenges and gives them practical insights that can inform their research.
- Industry Fellowships: Create fellowships where industry professionals can spend time in academic institutions, sharing their practical experience and learning about the latest research developments.
- Problem-Based Learning: Integrate real-world industrial problems into the curriculum. Students can work on these as part of their coursework, bridging the gap between theoretical learning and practical application.
- Guest Lectures and Workshops: Invite industry professionals to give guest lectures or conduct workshops, bringing practical insights into the academic setting.
- University Research Centers: Establish research centers within universities that focus specifically on applied research. These centers can serve as hubs for industry-academic collaboration, focusing on solving practical engineering problems.
- Technology Transfer Offices: Universities can set up offices dedicated to technology transfer, helping to commercialize academic research and bring it to the market.
- Industry-Academic Roles: Encourage professionals to pursue dual careers in both academia and industry. For example, an academic might spend part of their time conducting research at a university and part of their time consulting for industry.
- Adjunct Professorships: Industry professionals can be appointed as adjunct professors, allowing them to contribute to academic teaching and research while remaining active in the industry.
- Joint Funding Programs: Governments and funding bodies can create programs that specifically support projects involving both academic institutions and industrial partners.
- Innovation Grants: Provide grants for collaborative projects that require academic research to be applied in an industrial context. This encourages both parties to work together toward a common goal.
- Conferences and Workshops: Organize events that bring together academics and industry professionals to share knowledge, discuss challenges, and explore collaborative opportunities.
- Online Platforms: Create online forums, databases, and platforms where industry and academia can share research findings, case studies, and best practices.
- Industry-Driven Curriculum: Involve industry representatives in curriculum development to ensure that academic programs are aligned with current industry needs and trends.
- Continuous Education Programs: Offer continuing education and professional development programs that allow industry professionals to stay updated with the latest academic research and engineering advancements.
- Post-Implementation Feedback: After implementing academic research in an industrial setting, gather feedback on its effectiveness. This feedback can inform future research and help academics understand the practical challenges of implementation.
- Industry Advisory Boards: Establish industry advisory boards for academic departments. These boards can provide insights into current industry needs and guide academic research priorities.
- Incubators and Accelerators: Universities can establish incubators and accelerators that support the commercialization of academic research. These can provide resources, mentorship, and connections to industry.
- Spin-Off Companies: Encourage the creation of spin-off companies from academic research, which can directly apply innovative ideas in a commercial context.
- Document and Share Successes: Publish case studies and applied research papers that detail successful industry-academic collaborations. Sharing these success stories can inspire more partnerships.
- Applied Engineering Journals: Promote the creation or use of academic journals that focus specifically on applied engineering, where research findings are directly related to industrial applications.
By implementing these strategies, the gap between academic and industrial engineering can be significantly reduced, leading to more effective innovation and practical outcomes that benefit both academia and industry.

Several countries have developed their own rockets capable of launching payloads into space. These countries have invested in space programs that include the design, testing, and deployment of orbital rockets. Here is a list of countries that have successfully built and launched such rockets:
1. United States- Notable Rockets: Saturn V, Space Shuttle, Falcon 9, Delta IV, Atlas V, SLS (Space Launch System)
- Space Agency: NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
- Private Companies: SpaceX, Blue Origin, United Launch Alliance (ULA)
- Notable Rockets: R-7 (Soyuz), Proton, Zenit, Angara
- Space Agency: Roscosmos (Russian Federal Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: Long March series (Chang Zheng), including Long March 3B, Long March 5
- Space Agency: CNSA (China National Space Administration)
- Notable Rockets: Ariane series (Ariane 5, Ariane 6)
- Space Agency: CNES (National Centre for Space Studies) and ESA (European Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: H-IIA, H-IIB, Epsilon
- Space Agency: JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency)
- Notable Rockets: PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle), GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle)
- Space Agency: ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)
- Notable Rockets: Shavit
- Space Agency: ISA (Israel Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: Safir, Simorgh
- Space Agency: ISA (Iranian Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: Unha series (derived from Taepodong-2)
- Space Agency: NADA (National Aerospace Development Administration)
- Notable Rockets: Naro-1, KSLV-II (Nuri)
- Space Agency: KARI (Korea Aerospace Research Institute)
- Notable Rockets: Black Arrow (historical; UK no longer has an active national rocket program but is involved in international collaborations)
- Space Agency: UKSA (UK Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: VLS-1 (program was developed but not fully successful; Brazil is still active in space technology development)
- Space Agency: AEB (Brazilian Space Agency)
- Notable Rockets: Zenit, Tsyklon (inherited from Soviet-era technologies, Ukraine continues to develop space technologies)
- Space Agency: SSAU (State Space Agency of Ukraine)
In addition to the countries listed above, several other nations are actively developing or have developed rocket technology with varying degrees of success, including:
- Turkey: Developing the Gokturk series of rockets.
- United Arab Emirates: Partnering with other nations, with ambitions for indigenous rocket development.
- Australia: Developing the capability for launching small satellites.
These countries have made significant investments in their space programs, developing the necessary infrastructure, technology, and expertise to build and launch rockets capable of reaching space. The list is evolving as more nations seek to develop or expand their space capabilities, reflecting the growing global interest in space exploration and satellite deployment.
Drones are playing a pivotal role in the evolution of unmanned farms by providing a range of capabilities that enhance precision agriculture, improve farm management, and increase overall efficiency. Here’s how drones are contributing to the development of unmanned farms:

- Aerial Surveillance: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors can capture detailed images of crops from above. These images help farmers monitor crop health, identify stressed areas, and detect issues like nutrient deficiencies, disease, or pest infestations.
- Early Detection: By regularly surveying fields, drones can spot early signs of problems, allowing farmers to take corrective action before issues become widespread. This leads to better crop management and higher yields.
- Targeted Spraying: Drones can be used for precision spraying of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. They can apply these substances only where needed, reducing chemical use and minimizing environmental impact.
- Variable Rate Application: Drones can be programmed to adjust the application rate of inputs based on the specific needs of different areas within a field. This ensures that each part of the field receives the optimal amount of treatment, leading to more uniform crop growth and better resource utilization.
- Aerial Seeding: Some drones are capable of dropping seeds directly into the soil, enabling aerial seeding of crops, especially in difficult-to-reach or rugged terrain. This is particularly useful for reforestation efforts or planting cover crops.
- Precision Planting: Drones equipped with seed dispensers can plant seeds with high precision, ensuring even distribution and optimal spacing for crop growth.
- Soil Mapping: Drones can carry sensors that measure soil properties, such as moisture content, temperature, and nutrient levels. This data is used to create detailed soil maps, helping farmers understand soil variability and make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and crop rotation.
- Topographic Mapping: By creating 3D maps of the terrain, drones help farmers plan more effective irrigation systems, manage water flow, and prevent soil erosion.
- Water Stress Detection: Drones equipped with thermal cameras can detect water stress in crops by identifying temperature variations. This helps farmers optimize irrigation schedules and ensure that crops receive adequate water.
- Monitoring Irrigation Systems: Drones can fly over irrigation systems to check for leaks, blockages, or inefficiencies, ensuring that water is being distributed evenly and effectively across the farm.
- Real-Time Data: Drones provide real-time data on various aspects of farm operations, enabling quick decision-making. The data collected can be analyzed to identify trends, predict yields, and optimize resource allocation.
- Integration with AI and IoT: Drones can be integrated into broader IoT systems on the farm, working in conjunction with ground-based sensors and automated machinery. AI algorithms can analyze drone data to provide actionable insights, making farm management more precise and efficient.
- Accurate Field Maps: Drones create accurate maps of fields, including boundaries, crop zones, and infrastructure. These maps are essential for planning and optimizing farm operations, especially in large or complex fields.
- Plant Counting and Density Measurement: Drones can count individual plants and measure plant density across fields, helping farmers monitor crop establishment and adjust planting strategies as needed.
- Crop Maturity Assessment: Drones can monitor crop maturity levels across large fields, helping farmers determine the optimal time for harvesting. This ensures that crops are harvested at peak quality and reduces the risk of losses.
- Guiding Autonomous Harvesters: Drones can provide aerial views and data that guide autonomous harvesting machines, improving the efficiency and accuracy of the harvest.
- Herd Surveillance: Drones can be used to monitor livestock, tracking their movements, health, and behavior. This is especially useful for managing large herds or in difficult terrain.
- Grazing Management: By monitoring pasture conditions and livestock distribution, drones help farmers manage grazing patterns, ensuring sustainable use of grazing lands.
- Climate and Weather Data: Drones can be equipped with sensors to monitor local climate and weather conditions, helping farmers adapt to changing conditions and plan their activities accordingly.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health: Drones can be used to monitor the biodiversity and health of ecosystems on and around the farm, ensuring that farming practices are environmentally sustainable.
Drones are transforming unmanned farms by providing critical data, enabling precision agriculture, and automating various tasks. They allow for more efficient resource use, reduce labor costs, and increase crop yields, making farming more sustainable and profitable. As drone technology continues to evolve, it will likely become an even more integral part of modern agriculture, driving further innovation and efficiency in unmanned farms.
## Embracing CI/CD: Transforming Software Development
In today's fast-paced software development landscape, the demand for rapid delivery and high-quality applications has never been greater. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) have emerged as essential practices that help teams meet these demands. This article explores the fundamentals of CI/CD, its benefits, and best practices for implementation.
### What is CI/CD?**
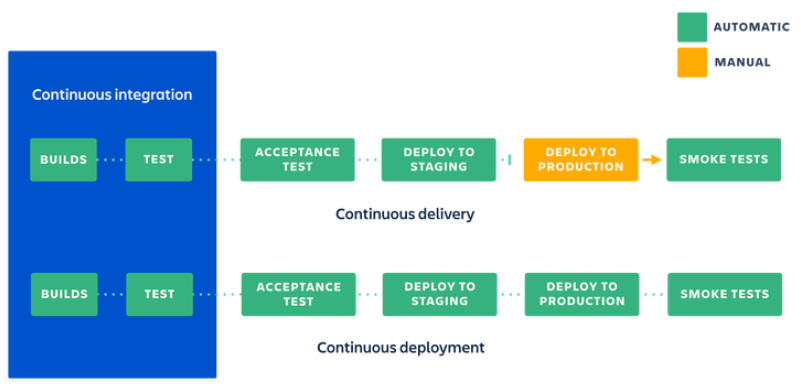
**Continuous Integration (CI)** is a development practice where code changes are automatically integrated into a shared repository several times a day. Each integration is verified by an automated build and testing process, allowing teams to detect errors quickly and improve software quality.
**Continuous Delivery (CD)** extends CI by ensuring that code changes are automatically prepared for a production release. This means that every change that passes automated tests can be deployed to production at any time, making the release process more predictable and less risky.
**Continuous Deployment** takes this a step further by automatically deploying every change that passes the tests to production, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
### Benefits of CI/CD
1. **Faster Time to Market**: By automating the integration and delivery processes, teams can release new features and updates more quickly, responding to customer needs and market changes in real time.
2. **Improved Code Quality**: Automated testing ensures that code changes are validated before they are merged, reducing the likelihood of bugs and improving overall software quality.
3. **Reduced Risk**: Smaller, incremental updates are easier to manage and roll back if issues arise. This minimizes the risk associated with large releases and helps maintain system stability.
4. **Enhanced Collaboration**: CI/CD fosters a culture of collaboration among development, operations, and quality assurance teams. Everyone works together towards a common goal of delivering high-quality software efficiently.
5. **Greater Customer Satisfaction**: With faster releases and higher quality, teams can better meet customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
### Key Components of CI/CD
1. **Version Control System (VCS)**: A VCS like Git is essential for managing code changes and facilitating collaboration among developers.
2. **Automated Build Tools**: Tools such as Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitHub Actions automate the process of compiling code and running tests, ensuring that changes are validated quickly.
3. **Automated Testing**: Implementing unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests helps catch bugs early in the development process.
4. **Deployment Automation**: Tools like Kubernetes, Docker, and cloud services enable automated deployment to various environments, ensuring consistency and reliability.
5. **Monitoring and Feedback**: Continuous monitoring of applications in production allows teams to gather feedback and address issues proactively.
### Best Practices for Implementing CI/CD
1. **Start Small**: Begin with a single project or team to implement CI/CD practices. Gradually expand to other projects as the team gains experience.
2. **Automate Everything**: Aim to automate as many processes as possible, including builds, tests, and deployments. This reduces manual errors and speeds up the workflow.
3. **Maintain a Clean Codebase**: Encourage developers to write clean, maintainable code and adhere to coding standards. This makes it easier to integrate changes and reduces the likelihood of bugs.
4. **Use Feature Flags**: Implement feature flags to allow for gradual rollouts of new features. This enables teams to test new functionality in production without impacting all users.
5. **Continuously Monitor and Improve**: Regularly review CI/CD processes and gather feedback from the team. Look for areas to optimize and improve efficiency.
### Conclusion
CI/CD is not just a set of tools; it’s a cultural shift that transforms how software is developed and delivered. By embracing CI/CD practices, organizations can achieve faster delivery, improved quality, and greater collaboration among teams. As the software landscape continues to evolve, adopting CI/CD will be crucial for staying competitive and meeting the ever-changing demands of customers.
In the end, the journey to CI/CD is an ongoing process of learning and improvement, but the rewards are well worth the effort. Embrace the change, and watch your development process transform!




.jpeg)

.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)


.jpeg)